成果
2025
- VLDBJEfficiently Counting Four-Node Motifs in Large-Scale Temporal GraphsZhihao Zhang#, Jianpeng Qi#*, Lei Cao , and 2 more authorsThe VLDB Jounral. More Information can be found here , May 2025
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术会议-数据库/数据挖掘/内容检索A类
Temporal motifs are compact subgraph patterns that recur frequently within a sequence of timestamps. They reveal implicit insights in the graph data and guide informed decision-making. However, current methods for exactly counting temporal motifs face challenges of high time complexity and inapplicability when motifs involve four nodes and struggle to scale to larger temporal graphs. In this paper, we propose a novel and exact counting framework tailored to 4-node, 3-edge, and 4-edge single-interaction temporal motifs whose time window size is constrained in a fixed interval. To speed up the counting process, we begin by categorizing all 4-node temporal motifs based on their structural characteristics. Subsequently, we present three rapid and precise sub-algorithms, each dedicated to counting motifs within its category. To expedite the counting process, we implement a series of straightforward and highly effective counters. Our algorithm cleverly uses these counters to identify and record all temporal motif instances based on the information and interrelationships of edges, significantly enhancing counting efficiency, especially for large-scale temporal graphs. Our extensive experiments on 14 large-scale real-world temporal graphs demonstrate the superiority of our work in terms of efficiency. Results show that our work significantly outperforms all state-of-the-art baselines and achieves a remarkable speedup of up to 25,816-fold.
@article{vldbj2025mc, title = {Efficiently Counting Four-Node Motifs in Large-Scale Temporal Graphs}, author = {Zhang#, Zhihao and Qi#, Jianpeng and Cao, Lei and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, journal = {The VLDB Jounral}, volume = {34}, number = {44}, pages = {1-27}, year = {2025}, month = may, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/s00778-025-00926-8}, url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00778-025-00926-8}, } - $\text MA^2\text Traj $: Diffusion network with multi-attribute aggregation for trajectory generationXingyu Zhao, Xiao Zhang, Bohan Zhang , and 3 more authorsGeoInformatica, May 2025
With the rapid development of GPS devices and mobile internet technology, trajectory data has generated immense value but also raised concerns about privacy leakage. Existing trajectory generation models utilize users’ trip attributes to provide auxiliary associations for GPS trajectories, yet they overlook the spatial constraints of users’ trip patterns. Additionally, matching the road network with trajectories results in time consumption. To address these issues, we propose a diffusion network with multi-attribute aggregation for trajectory generation, named $\varvec\text MA^2\text Traj$. Specifically, we introduce origin-destination information to provide spatial constraints for trip attributes. Meanwhile, we design a multi-attribute aggregation module, which integrates origin-destination information and trip attributes (such as trip distance and average speed) to effectively capture user trip patterns and spatial distribution, thereby enhancing the reliability of trajectory generation. Experimental results show that our model achieves a 4.8% performance improvement, significantly enhancing the accuracy of trajectory generation.
@article{RN2764, author = {Zhao, Xingyu and Zhang, Xiao and Zhang, Bohan and Qi, Jianpeng and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, title = {$$\text {MA}^{2}\text {Traj} $$: Diffusion network with multi-attribute aggregation for trajectory generation}, journal = {GeoInformatica}, doi = {10.1007/s10707-025-00549-9}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/s10707-025-00549-9}, year = {2025}, } - ICDE25UMGAD: Unsupervised Multiplex Graph Anomaly DetectionXiang Li, Jianpeng Qi, Zhongying Zhao , and 4 more authorsIn the 41th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering , May 2025
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术会议-数据库/数据挖掘/内容检索A类
@inproceedings{icde2025, author = {Li, Xiang and Qi, Jianpeng and Zhao, Zhongying and Zheng, Guanjie and Cao, Lei and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, booktitle = {the 41th IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering}, title = {UMGAD: Unsupervised Multiplex Graph Anomaly Detection}, year = {2025}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {}, } - Efficient Information Updates in Compute-First Networking via Reinforcement Learning with Joint AoI and VoIJianpeng Qi, Chao Liu, Chengxiang Xu , and 3 more authorsarXiv. More Information can be found here , May 2025
Timely and efficient dissemination of service information is critical in compute-first networking systems, where user requests arrive dynamically and computing resources are constrained. In such systems, the access point (AP) plays a key role in forwarding user requests to a server based on its latest received service information. This paper considers a single-source, single-destination system and introduces an Age-and-Value-Aware (AVA) metric that jointly captures both the timeliness and the task relevance of service information. Unlike traditional freshness-based metrics, AVA explicitly incorporates variations in server-side service capacity and AP forwarding decisions, allowing more context-aware update evaluation. Building upon AVA, we propose a reinforcement learning-based update policy that learns to selectively transmit service information updates to the AP. It aims to maximize overall task success while minimizing unnecessary communications. Extensive simulations under diverse user request patterns and varying service capacities demonstrate that AVA reduces the update frequency by over 90% on average compared to baselines, with reductions reaching 98% in certain configurations. Crucially, this reduction is achieved without compromising the accuracy of task execution or the quality of decision making.
@article{qi2025efficientinformationupdatescomputefirst, title = {Efficient Information Updates in Compute-First Networking via Reinforcement Learning with Joint AoI and VoI}, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Liu, Chao and Xu, Chengxiang and Wang, Rui and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, year = {2025}, journal = {arXiv}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.06025}, } - arXivA Survey on Open-Source Edge Computing Simulators and Emulators: The Computing and Networking Convergence PerspectiveJianpeng Qi, Chao Liu, Xiao Zhang , and 4 more authors. More Information can be found here , May 2025
Edge computing, with its low latency, dynamic scalability, and location awareness, along with the convergence of computing and communication paradigms, has been successfully applied in critical domains such as industrial IoT, smart healthcare, smart homes, and public safety. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of open-source edge computing simulators and emulators, presented in our GitHub repository (https://github.com/qijianpeng/awesome-edge-computing), emphasizing the convergence of computing and networking paradigms. By examining more than 40 tools, including CloudSim, NS-3, and others, we identify the strengths and limitations in simulating and emulating edge environments. This survey classifies these tools into three categories: packet-level, application-level, and emulators. Furthermore, we evaluate them across five dimensions, ranging from resource representation to resource utilization. The survey highlights the integration of different computing paradigms, packet processing capabilities, support for edge environments, user-defined metric interfaces, and scenario visualization. The findings aim to guide researchers in selecting appropriate tools for developing and validating advanced computing and networking technologies.
@misc{qi2025surveyopensourceedgecomputing, title = {A Survey on Open-Source Edge Computing Simulators and Emulators: The Computing and Networking Convergence Perspective}, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Liu, Chao and Zhang, Xiao and Wang, Lei and Wang, Rui and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, year = {2025}, journal = {arXiv}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09995}, }
2024
- TPAoI: Ensuring Fresh Service Status at the Network Edge in Compute-First NetworkingHaosheng He#, Jianpeng Qi#, Chao Liu , and 2 more authorsarXiv. More Information can be found here , May 2024
@article{he2024tpaoiensuringfreshservice, title = {TPAoI: Ensuring Fresh Service Status at the Network Edge in Compute-First Networking}, author = {He#, Haosheng and Qi#, Jianpeng and Liu, Chao and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, year = {2024}, journal = {arXiv}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.18391}, } - AutoSculpt: A Pattern-based Model Auto-pruning Framework Using Reinforcement Learning and Graph LearningLixian Jing#, Jianpeng Qi#, Junyu Dong , and 1 more author. More Information can be found here , May 2024
@misc{jing2024autosculptpatternbasedmodelautopruning, title = {AutoSculpt: A Pattern-based Model Auto-pruning Framework Using Reinforcement Learning and Graph Learning}, author = {Jing#, Lixian and Qi#, Jianpeng and Dong, Junyu and Yu, Yanwei}, year = {2024}, journal = {arXiv}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.18091}, } - MoTTo: Scalable motif counting with time-aware topology constraint for large-scale temporal graphsJiantao Li#, Jianpeng Qi#, Yueling Huang , and 3 more authorsIn the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM) , May 2024
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术会议-数据库/数据挖掘/内容检索B类
@inproceedings{motto2024cikm, author = {Li#, Jiantao and Qi#, Jianpeng and Huang, Yueling and Cao, Lei and Yu, Yanwei and Dong, Junyu}, booktitle = {the 33rd ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management (CIKM)}, title = {MoTTo: Scalable motif counting with time-aware topology constraint for large-scale temporal graphs}, year = {2024}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {}, } - EasiEI: A simulator to flexibly modeling complex edge computing environmentsXiao Su#, Jianpeng Qi# , Jiahao Wang , and 1 more authorIEEE Internet of Things Journal. More Information can be found here , Jun 2024
中科院一区Top
In edge computing scenarios, there is a need for modeling dedicated features and heterogeneous devices functions, as well as integrating multiple complex scenarios with diverse objectives and frequent interactions. However, existing platforms modeling for the whole device ignores the independence between functional components resulting in limited scenario support. We propose an open-source simulator named EasiEI. EasiEI addresses the need for higher level feature replaceability and independence in modeling complex edge scenarios through independent functional component-level modeling and microkernel architecture. This approach enables users to assemble independent functional components in a plug-and-play manner for heterogeneous devices or different application requirements. EasiEI is fully compatible with all the existing built-in modules in NS3 (a powerful network discrete event simulator). To verify the flexibility and extensibility of EasiEI, we implement several centralized and decentralized computing paradigms cases in a step-by-step way. These cases restore and simulate the performance state of various real devices in real time, meeting the requirements for verifying the edge computing ideas such as task scheduling in a distributed manner. Results show that the simulations have well reflected the characteristics of the real world and can construct complex environment flexibly.
@article{easiei2024iotj, title = {EasiEI: A simulator to flexibly modeling complex edge computing environments}, author = {Su#, Xiao and Qi#, Jianpeng and Wang, Jiahao and Wang, Rui}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, volume = {11}, pages = {1558-1571}, number = {1}, year = {2024}, month = jun, publisher = {IEEE}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2023.3289870}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10164279}, google_scholar_id = {qUcmZB5y_30C}, } - Towards distributively build time-sensitive-service coverage in compute first networkingJianpeng Qi, Xiao Su, and Rui WangIEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking. More Information can be found here , Jun 2024
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊-计算机网络-A类
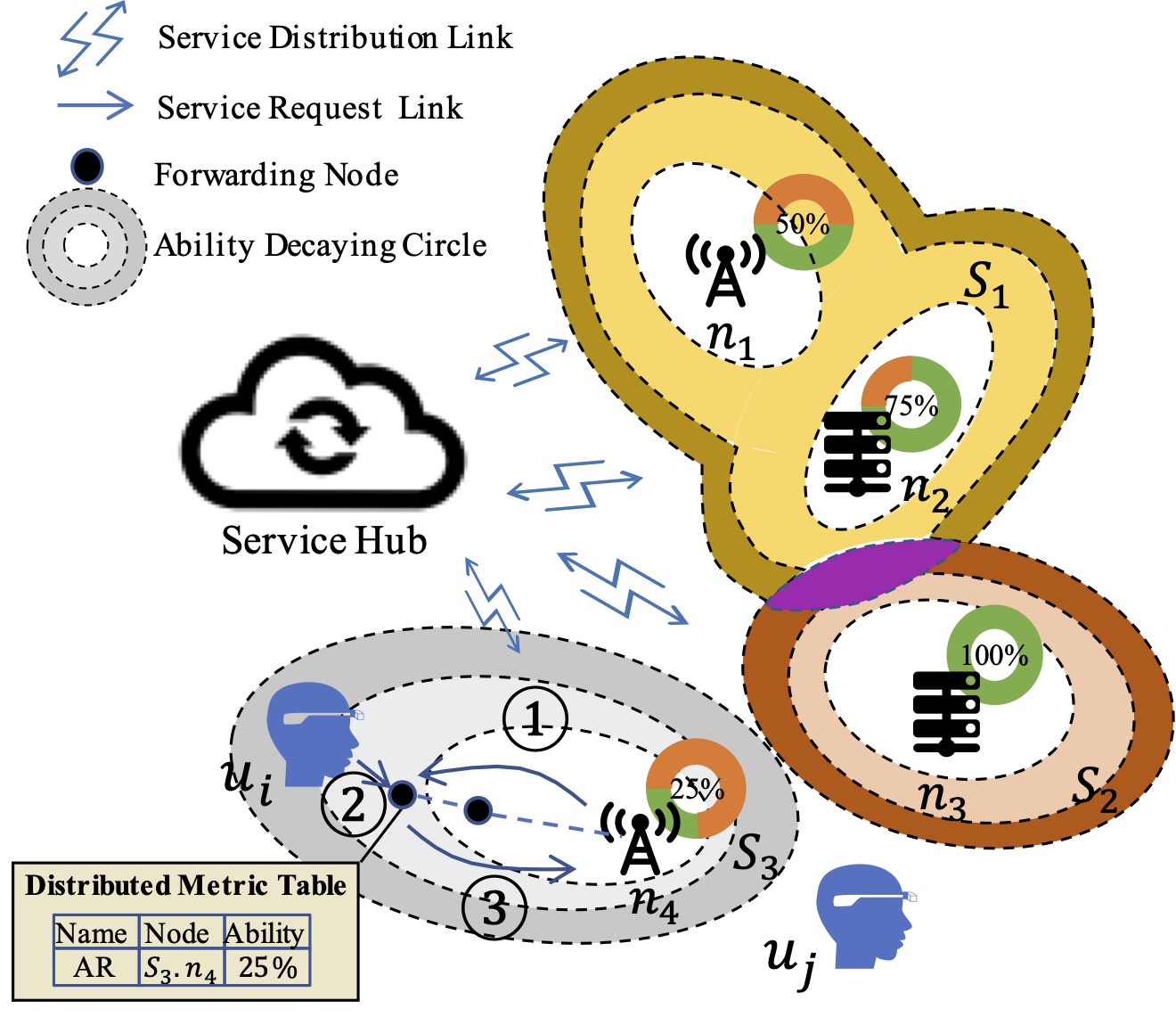
Despite placing services and computing resources at the edge of the network for ultra-low latency, we still face the challenge of centralized scheduling costs, including delays from additional request forwarding and resource selection. To address this challenge, we propose SmartBuoy, a new computing paradigm. Our approach starts with a service coverage concept that assumes users within the coverage have high access availability. To enable users to perceive service status, we design a distributed metric table that synchronizes service status periodically and distributively. We propose coverage indicator updating principles to make the updating process more effective. We then implement two distributed methods, SmartBuoy-Time and SmartBuoy-Reliability, that enable users to perceive service capability directly and immediately. To determine the metric table update window size, we provide an analysis method based on user access patterns and offer a theoretical upper bound in a dynamic environment, making SmartBuoy easy to use. Finally, we implement the proposed methods distributively on an open-source edge computing simulator. Experiments on a real-world network topology dataset demonstrate the efficiency of SmartBuoy in reducing delays and improving the success rate.
@article{smartbuoy2024tnet, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Su, Xiao and Wang, Rui}, title = {Towards distributively build time-sensitive-service coverage in compute first networking}, journal = {IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking}, volume = {32}, publisher = {IEEE}, number = {1}, pages = {582-597}, doi = {10.1109/TNET.2023.3289830}, year = {2024}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10172050/}, google_scholar_id = {hC7cP41nSMkC}, } - ECML-PKDDHierarchical graph contrastive learning for review-enhanced recommendationChangsheng Shui, Xiang Li, Jianpeng Qi , and 2 more authorsIn Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML-PKDD 2024) , Jun 2024
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术会议-数据库/数据挖掘/内容检索B类
@inproceedings{changsheng24pkdd, author = {Shui, Changsheng and Li, Xiang and Qi, Jianpeng and Jiang, Guiyuan and Yu, Yanwei}, booktitle = {Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML-PKDD 2024)}, title = {Hierarchical graph contrastive learning for review-enhanced recommendation}, year = {2024}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {423-440}, publisher = {Springer}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-031-70365-2_25}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-70365-2_25}, } - Patent一种网络信息平台中异常用户检测方法及系统于彦伟, 陈怡辛, 齐建鹏 , and 1 more authorJun 2024
2023
- R2: A distributed remote function execution mechanism with built-in metadataJianpeng Qi, and Rui WangIEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking. More Information can be found here , Jun 2023
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊-计算机网络-A类
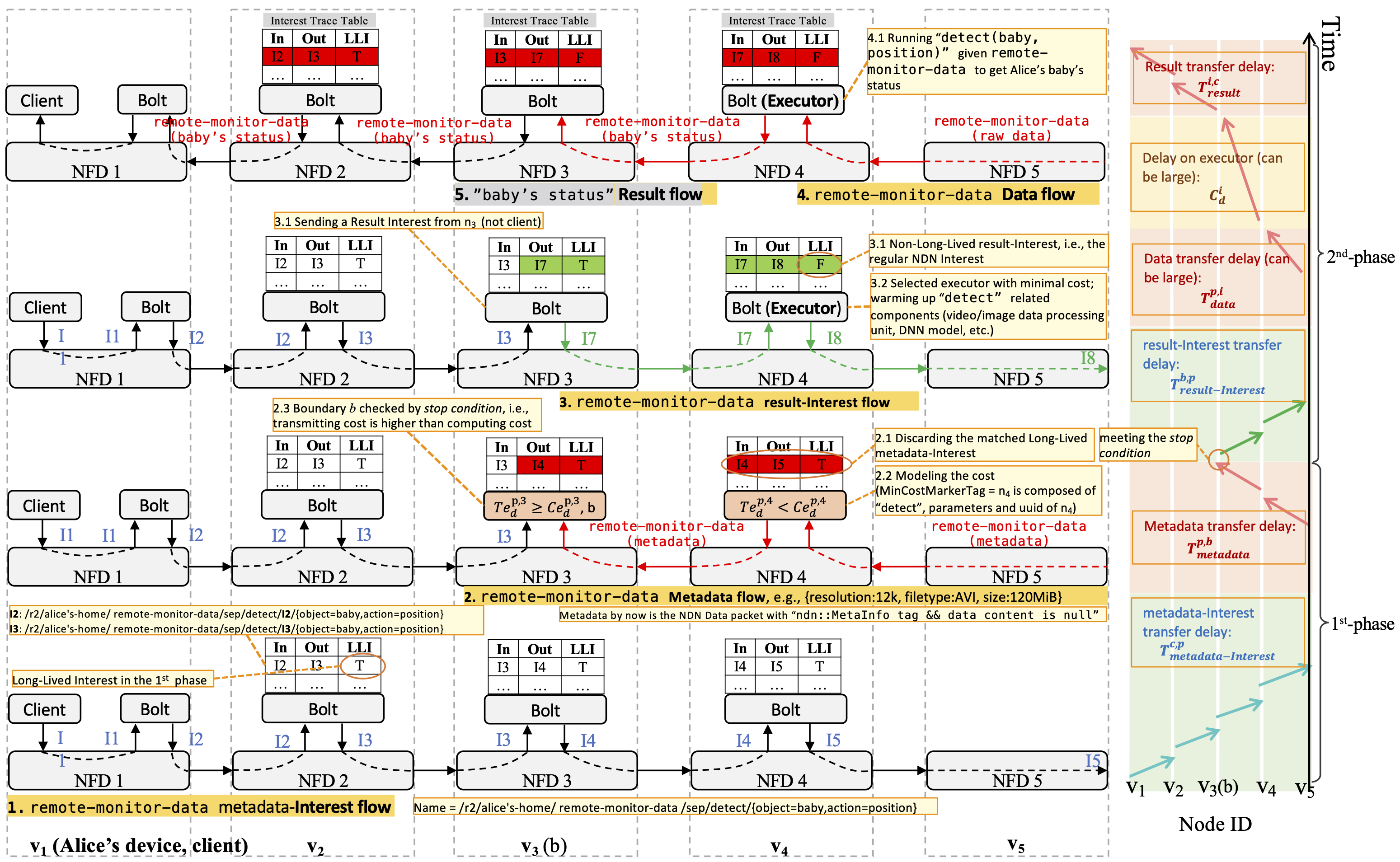
Named data networking (NDN) constructs a network by names, providing a flexible and decentralized way to manage resources within the edge computing continuum. This paper aims to solve the question, “Given a function with its parameters and metadata, how to select the executor in a distributed manner and obtain the result in NDN?” To answer it, we design R2 that involves the following stages. First, we design a name structure including data, function names, and other function parameters. Second, we develop a 2-phase mechanism, where in the first phase, the function request from a client-first reaches the data source and retrieves the metadata. Then the best node is selected while the metadata responds to the client. In the second phase, the chosen node directly retrieves the data, executes the function, and provides the result to the client. Furthermore, we propose a stop condition to intelligently reduce the processing time of the first phase and provide a simple proof and range analysis. Simulations confirm that R2 outperforms the current solutions in terms of resource allocation, especially when the data volume and the function complexity are high. In the experiments, when the data size is 100 KiB and the function complexity is O(n2) , the speedup ratio is 4.61. To further evaluate R2, we also implement a general intermediate data processing logic named “Bolt” implemented on an app-level in ndnSIM. We believe that R2 shall help the researchers and developers to verify their ideas smoothly.
@article{r22023tnet, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Wang, Rui}, title = {R2: A distributed remote function execution mechanism with built-in metadata}, journal = {IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking}, publisher = {IEEE}, volume = {31}, year = {2023}, number = {24}, pages = {710-723}, doi = {10.1109/TNET.2022.3198467}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1109/TNET.2022.3198467}, google_scholar_id = {aqlVkmm33-oC}, } - REMR: A reliability evaluation method for dynamic edge computing network under time constraintsLiang Chen#, Jianpeng Qi#, Xiao Su , and 1 more authorIEEE Internet of Things Journal, Mar 2023
中科院一区Top
Computation and/or communication-intensive collaborative services accompanied by several distributed tasks/components, such as the services in Internet of Things, can be anywhere nowadays. These services are usually used by users at the Internet edge, making cloud computing struggles with the high end-to-end latency. Thanks to edge computing which pushes resources to the edge, the goals with lower latency can be well satisfied. However, in actual scenarios especially under dynamic edge computing networks, changes exist in resources, including computing, bandwidth, and nodes. Meanwhile, data packets (or flow) among collaborative tasks/components of a service can also not be conserved. These characteristics lead the service reliability hard to be guaranteed and make existing reliability evaluation methods no longer accurate. To study the effect of distributed and collaborative service deployment strategies under such background, we propose a reliability evaluation method (REMR). We first look for the solution set which can meet the time constraints. Then, we calculate the reliability of service supported by the solution set based on the principle of inclusion–exclusion with distributions of available transmission bandwidth and computing resources. Finally, we provide an illustrative example with several real-world data sets to make REMR easy to follow. To make REMR more reliable, we also propose and implement a Monte Carlo simulation method. Experiments prove that the reliability calculated by REMR is nearly the same as the simulation results and both the latencies and the jitters are also at a lower level.
@article{remr2022iotj, author = {Chen#, Liang and Qi#, Jianpeng and Su, Xiao and Wang, Rui}, title = {REMR: A reliability evaluation method for dynamic edge computing network under time constraints}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, volume = {10}, number = {5}, pages = {4281-4291}, publisher = {IEEE}, month = mar, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10172050}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2022.3216056}, google_scholar_id = {mVmsd5A6BfQC}, year = {2023}, } -
 面向边缘智能的协同推理综述王睿, 齐建鹏, 陈亮 , and 1 more author计算机研究与发展, Mar 2023
面向边缘智能的协同推理综述王睿, 齐建鹏, 陈亮 , and 1 more author计算机研究与发展, Mar 2023近年来,信息技术的不断变革伴随数据量的急剧爆发,使主流的云计算解决方案面临实时性差、带宽受限、高能耗、维护费用高、隐私安全等问题. 边缘智能的出现与快速发展有效缓解了此类问题,它将用户需求处理下沉到边缘,避免了海量数据在网络中的流动,得到越来越多的关注. 由于边缘计算中资源性能普遍较低,通过资源实现协同推理正成为热点.通过对边缘智能发展的趋势分析,得出边缘协同推理目前仍处于增长期,还未进入稳定发展期. 因此,在对边缘协同推理进行充分调研的基础上,将边缘协同推理划分为智能化方法与协同推理架构2个部分,分别对其中涉及到的关键技术进行纵向归纳整理,并从动态场景角度出发,对每种关键技术进行深入分析,对不同关键技术进行横向比较以及适用场景分析.最后对动态场景下的边缘协同推理给出值得研究的若干发展方向.
@article{edgeintelligence2023jfyz, author = {王睿 and 齐建鹏 and 陈亮 and 杨龙}, title = {面向边缘智能的协同推理综述}, journal = {计算机研究与发展}, volume = {60}, pages = {398-414}, year = {2023}, issn = {1000-1239}, doi = {10.7544/issn1000-1239.202110867}, url = {https://crad.ict.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.7544/issn1000-1239.202110867}, } - 面向边缘智能的协同训练研究进展王睿, 王岩, 尹朴 , and 5 more authors工程科学学报, Mar 2023
http://digitalpaper.stdaily.com/http_www.kjrb.com/kjrb/html/2023-06/07/content_554339.htm?div=-1
2022
- The fluctuation analysis of public opinion energy: Modeling social group opinion base on the event of social networksYayong Shi, Jianpeng Qi, and Rui WangIntelligent Systems with Applications, Mar 2022
In the period of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), millions of people participate in the discussion of COVID-19 on the Internet, which can easily trigger public opinion and threaten social stability. To find out the relationship between the intergroup variability in numbers and perspectives and the dynamic change of the number of infected people, this paper defines the public focus level to quantify the level of attention of people to the information related to an epidemic situation, and the POF model based on the level of epidemic focus is proposed. In this paper, we have carried out simulation experiments in small-world networks and scale-free networks, respectively, to explore the relationship between the model parameters and the spreading range and speed of each population. Furthermore, the paper also analyzed all the original microblog posts published by the People’s Daily from January 14, 2020, to February 12, 2020, and compared the data simulated by the POF model with the real data from the People’s Daily, the simulation data and the real data can be well fitted to prove the reliability of the model.
@article{SHI2022200072, title = {The fluctuation analysis of public opinion energy: Modeling social group opinion base on the event of social networks}, journal = {Intelligent Systems with Applications}, volume = {14}, pages = {200072}, year = {2022}, issn = {2667-3053}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswa.2022.200072}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2667305322000138}, author = {Shi, Yayong and Qi, Jianpeng and Wang, Rui}, keywords = {Information spreading, Computer simulation, COVID-19, Spreading dynamics, Public focus level} }
2021
- A distributed swarm intelligence-based energy-saving method among massive edge nodesJianpeng Qi, Suli Ren , Boran Wang , and 1 more authorInternational Journal of Communication Systems, Mar 2021
Summary In edge computing, how to save energy among sustainable edge nodes is a hot topic. ON/OFF switching of edge nodes as a key point is efficient but still suffers from the long round-trip time problem because of its centralized control manner. Especially in the wireless network, service coverage is proved to be NP-Complete. To this end, we propose a Distributed Swarm intelligence-based Energy-saving algorithm (DSE). In DSE, pheromone and residual energy are used to calculate the wake-up probability. Through the wake-up probability, the edge node can be activated periodically and efficiently. In order to balance the energy in the whole system that contains massive edge nodes, we further use a correction factor, that is, DSE+, to adjust the wake-up probability of the nodes. The proposed methods allow for distributed implementation without requiring a centralized control by the coordinator, and the pheromone accumulated temporally and spatially. In addition, they do not require node localization. Experiments show that both DSE and DSE+ can work as expected, and DSE+ with the correction factor improves the lifetime of the whole system at least 12.6% compared with the DSE without the correction factor.
@article{dse2021ijcs, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Ren, Suli and Wang, Boran and Wang, Rui}, title = {A distributed swarm intelligence-based energy-saving method among massive edge nodes}, journal = {International Journal of Communication Systems}, volume = {34}, number = {17}, pages = {e4974}, keywords = {ant colony optimization, edge computing, energy-balanced framework, decentralized control, renewable energy sources}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.4974}, url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/dac.4974}, year = {2021}, google_scholar_id = {qxL8FJ1GzNcC} } - Anomaly Detection of Dust Removal System Through Gradient Boosting Decision Tree AlgorithmTao Yang, Liang Chen , Jigang Wang , and 2 more authorsIn 2021 International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE) , Mar 2021
@inproceedings{9445934, author = {Yang, Tao and Chen, Liang and Wang, Jigang and Cui, Zenghao and Qi, Jianpeng}, booktitle = {2021 International Conference on Communications, Information System and Computer Engineering (CISCE)}, title = {Anomaly Detection of Dust Removal System Through Gradient Boosting Decision Tree Algorithm}, year = {2021}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {685-688}, keywords = {Fault diagnosis;Fans;Computational modeling;Production;Predictive models;Boosting;Prediction algorithms;GBDT;K-means;Anomaly detection;Likelihood loss}, doi = {10.1109/CISCE52179.2021.9445934}, google_scholar_id = {_kc_bZDykSQC}, } - Patent一种分布式数据流中基于数据分布的负载均衡分发方法于彦伟, 齐建鹏, 刘兆伟 , and 1 more authorMar 2021
2020
- SMTS: A swarm intelligence-inspired sensor wake-up control method for multi-target sensing in wireless sensor networksJianpeng Qi, Lamei Pan, Suli Ren , and 2 more authorsWireless Networks, Mar 2020
中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊-计算机网络-C类
@article{smts2020wn, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Pan, Lamei and Ren, Suli and Chang, Fei and Wang, Rui}, title = {SMTS: A swarm intelligence-inspired sensor wake-up control method for multi-target sensing in wireless sensor networks}, journal = {Wireless Networks}, volume = {26}, issue = {5}, year = {2020}, pages = {3847-3859}, url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11276-020-02298-z}, doi = {10.1007/s11276-020-02298-z}, google_scholar_id = {dhFuZR0502QC}, } - Machinery health prognostics of dust removal fan data through deep neural networksTao Yang , Jigang Wang, Liang Chen , and 3 more authorsIn Cyberspace Data and Intelligence, and Cyber-Living, Syndrome, and Health , Mar 2020
In industrial production, the health of the machine is a very important issue. The health of the dust removal fan is a challenging issue in the field of ma-chine health. In this paper, the deep learning network Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network are combined to solve the health problem of the dust removal fan. The deep learning network VAE can map the features of the data to hidden variables, and the LSTM network can extract the time dependence between the data. Experiments show that the VAE-LSTM network is suitable for dust removal fans and has a good effect.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-981-33-4336-8_3, author = {Yang, Tao and Wang, Jigang and Chen, Liang and Cui, Zenghao and Qi, Jianpeng and Wang, Rui}, title = {Machinery health prognostics of dust removal fan data through deep neural networks}, booktitle = {Cyberspace Data and Intelligence, and Cyber-Living, Syndrome, and Health}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Springer Singapore}, address = {Singapore}, pages = {27--37}, }
2019
- 基于密度的 Top-n 局部异常点快速检测算法刘芳, 齐建鹏, 于彦伟 , and 2 more authors自动化学报, Mar 2019
局部异常检测 (Local outlier factor, LOF) 能够有效解决数据倾斜分布下的异常检测问题, 在很多应用领域具有较好的异常检测效果. 本文面向大数据异常检测, 提出了一种快速的 Top-n 局部异常点检测算法 MTLOF (Multi-granularity upper bound pruning based top-n LOF detection), 融合索引结构和多层 LOF 上界设计了多粒度的剪枝策略, 以快速发现 Top-n 局部异常点. 首先, 提出了四个更接近真实 LOF 值的上界, 以避免直接计算 LOF 值, 并对它们的计算复杂度进行了理论分析; 其次, 结合索引结构和 UB1, UB2 上界, 提出了两层的 Cell 剪枝策略, 不仅采用全局 Cell 剪枝策略, 还引入了基于 Cell 内部数据对象分布的局部剪枝策略, 有效解决了高密度区域的剪枝问题; 再次, 利用所提的 UB3 和 UB4 上界, 提出了两个更加合理有效的数据对象剪枝策略, UB3 和 UB4 上界更加接近于真实 LOF 值, 有利于剪枝更多数据对象, 而基于计算复用的上界计算方法, 大大降低了计算成本; 最后, 优化了初始 Top-n 局部异常点的选择方法, 利用区域划分和建立的索引结构, 在数据稀疏区域选择初始局部异常点, 有利于将 LOF 值较大的数据对象选为初始局部异常点, 有效提升初始剪枝临界值, 使得初始阶段剪枝掉更多的数据对象, 进一步提高检测效率. 在六个真实数据集上的综合实验评估验证 MTLOF 算法的高效性和可扩展性, 相比最新的 TOLF (Top-n LOF) 算法, 时间效率提升可高达 3.5 倍.
@article{topnoutlier2019zdh, author = {刘芳 and 齐建鹏 and 于彦伟 and 曹磊 and 赵金东}, title = {基于密度的 Top-n 局部异常点快速检测算法}, journal = {自动化学报}, volume = {45}, issue = {9}, pages = {1756-1771}, year = {2019}, google_scholar_id = {3fE2CSJIrl8C}, doi = {10.16383/j.aas.c180425}, url = {https://dx.doi.org/10.16383/j.aas.c180425} }
2017
- An effective and efficient hierarchical K-means clustering algorithmJianpeng Qi, Yanwei Yu , Lihong Wang , and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, Mar 2017
K-means plays an important role in different fields of data mining. However, k-means often becomes sensitive due to its random seeds selecting. Motivated by this, this article proposes an optimized k-means clustering method, named k*-means, along with three optimization principles. First, we propose a hierarchical optimization principle initialized by k* seeds (k*>k) to reduce the risk of random seeds selecting, and then use the proposed “top-n nearest clusters merging” to merge the nearest clusters in each round until the number of clusters reaches at k. Second, we propose an “optimized update principle” that leverages moved points updating incrementally instead of recalculating mean and SSE of cluster in k-means iteration to minimize computation cost. Third, we propose a strategy named “cluster pruning strategy” to improve efficiency of k-means. This strategy omits the farther clusters to shrink the adjustable space in each iteration. Experiments performed on real UCI and synthetic datasets verify the efficiency and effectiveness of our proposed algorithm.
@article{effective-kxmeans2017ijdsn, google_scholar_id = {Se3iqnhoufwC}, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Yu, Yanwei and Wang, Lihong and Liu, Jinglei and Wang, Yingjie}, title = {An effective and efficient hierarchical K-means clustering algorithm}, journal = {International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks}, volume = {13}, number = {8}, pages = {1550147717728627}, year = {2017}, doi = {10.1177/1550147717728627}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147717728627}, dimensions = {true} } - 移动社交网络异常签到在线检测算法赵冠哲, 齐建鹏, 于彦伟 , and 2 more authors智能系统学报, Mar 2017
随着智能手机, Pad 等智能移动设备的广泛普及, 移动社交网络的应用得到了快速发展. 本文针对移动社交网络中用户异常签到位置检测问题, 提出了一类基于用户移动行为特征的异常签到在线检测方法. 首先, 在基于距离的异常模型基础上, 提出了基于历史位置 (H-Outlier) 和基于好友圈 (F-Outlier) 两种异常签到模型; 然后, 针对 H-Outlier 提出了一种优化的检测算法 H-Opt, 利用所提的签到状态模型与优化的邻居搜索机制降低检测时间; 针对 F-Outlier 提出了一种基于触发的优化检测算法 F-Opt, 将连续的在线异常检测转化成了基于触发的异常检测方式; 最后, 在真实的移动社交网络用户签到数据集上, 验证了所提算法的有效性. 实验结果显示, F-Opt 显著降低了 H-Opt 的异常检测错误率; 同时, 相比于 LUE 算法, F-Opt 和 H-Opt 的效率分别平均提升了 2.34 倍和 2.45 倍.
@article{topnoutlier2019zdi, author = {赵冠哲 and 齐建鹏 and 于彦伟 and 刘兆伟 and 宋鹏}, title = {移动社交网络异常签到在线检测算法}, journal = {智能系统学报}, volume = {12}, issue = {5}, pages = {752-759}, year = {2017}, google_scholar_id = {8k81kl-MbHgC}, doi = {10.11992/tis.201706027}, url = {https://tis.hrbeu.edu.cn/oa/darticle.aspx?type=view&id=201706027} }
2016
- K*-Means: An Effective and Efficient K-Means Clustering AlgorithmJianpeng Qi, Yanwei Yu , Lihong Wang , and 1 more authorIn 2016 IEEE International Conferences on Big Data and Cloud Computing (BDCloud), Social Computing and Networking (SocialCom), Sustainable Computing and Communications (SustainCom) (BDCloud-SocialCom-SustainCom) , Mar 2016
K-means is a widely used clustering algorithm in field of data mining across different disciplines in the past fifty years. However, k-means heavily depends on the position of initial centers, and the chosen starting centers randomly may lead to poor quality of clustering. Motivated by this, this paper proposes an optimized k-means clustering method along with three optimization principles named k*-means. First, we propose a hierarchical optimization principle initialized by k* cluster centers (k* > k) to reduce the risk of randomly seeds selection, and then utilize proposed top-n method to merge the nearest clusters associated with the shortest n edges in each round until the number of clusters reaches at k. Second, we propose a cluster pruning strategy for improving efficiency of k-means by omitting the farther clusters to shrink the adjustable searching space for each point in each iteration. Third, we implement an optimized update theory to optimize the k-means iteration updating, which leverages moved points updating instead of recalculating mean and SSE of cluster to minimize computation cost. Our comprehensive experimental studies, using 2 synthetic datasets and 4 real world datasets from the UCI Machine Learning Repository, demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both effectiveness and efficiency.
@inproceedings{kxmeans2016bdcloud, author = {Qi, Jianpeng and Yu, Yanwei and Wang, Lihong and Liu, Jinglei}, booktitle = {2016 IEEE International Conferences on Big Data and Cloud Computing (BDCloud), Social Computing and Networking (SocialCom), Sustainable Computing and Communications (SustainCom) (BDCloud-SocialCom-SustainCom)}, title = {K*-Means: An Effective and Efficient K-Means Clustering Algorithm}, year = {2016}, volume = {}, google_scholar_id = {eQOLeE2rZwMC}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7723700}, number = {}, pages = {242-249}, doi = {10.1109/BDCloud-SocialCom-SustainCom.2016.46}, dimensions = {true} } - MR-Swarm: Mining swarms from big spatio-temporal trajectories using MapReduceYanwei Yu, Jianpeng Qi, Yunhui Lu , and 2 more authorsIn Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning – IDEAL 2016 , Mar 2016
The increasing pervasiveness of object tracking technologies has enabled collection of huge amount of spatio-temporal trajectories. Discovering the useful movement patterns from such big data is gaining in importance and challenging. In this paper we propose an distributed mining framework on Hadoop for efficiently discovering swarm patterns from big spatio-temporal trajectories in parallel. We first define the notion of maximal objectset that captures swarms by recombining clusters in timeset domain. Second, we propose a parallel model based on timeset independent property of swarm pattern to parallel the mining process. Furthermore we propose a distributed algorithm using MapReduce chain architecture based on the proposed parallel model, which features two optimization pruning strategies designed to minimize the computation costs. Our empirical study on the real Taxi dataset demonstrates its effectiveness in finding object-closed swarms. Extensive experiments on 5 network-connected workstations also validate that our proposed algorithm nearly achieves 5-fold speedups against the serial solution.
@inproceedings{10.1007/978-3-319-46257-8_61, author = {Yu, Yanwei and Qi, Jianpeng and Lu, Yunhui and Zhang, Yonggang and Liu, Zhaowei}, title = {MR-Swarm: Mining swarms from big spatio-temporal trajectories using MapReduce}, booktitle = {Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning -- IDEAL 2016}, year = {2016}, publisher = {Springer International Publishing}, address = {Cham}, pages = {568--575}, isbn = {978-3-319-46257-8}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46257-8_61}, doi = {10.1007/978-3-319-46257-8_61}, google_scholar_id = {WF5omc3nYNoC} } - 时空轨迹大数据分布式蜂群模式挖掘算法于彦伟, 齐建鹏, 陆云辉 , and 3 more authors计算机工程与科学, Mar 2016
@article{于彦伟2016时空轨迹大数据分布式蜂群模式挖掘算法, title = {时空轨迹大数据分布式蜂群模式挖掘算法}, author = {于彦伟 and 齐建鹏 and 陆云辉 and 赵金东 and 张永刚 and others}, journal = {计算机工程与科学}, volume = {38}, number = {02}, pages = {255}, year = {2016}, } - 面向不确定移动对象的连续 K 近邻查询算法于彦伟, 齐建鹏, 宋鹏 , and 1 more author模式识别与人工智能, Mar 2016
@article{于彦伟2016面向不确定移动对象的连续, title = {面向不确定移动对象的连续 K 近邻查询算法}, author = {于彦伟 and 齐建鹏 and 宋鹏 and 张永刚}, journal = {模式识别与人工智能}, volume = {29}, number = {11}, pages = {1048--1056}, year = {2016}, }